Abstract: In this piece we look at the hash-rate oscillations between Litecoin (LTC) and Dogecoin (DOGE) in 2014. We compare it to the current Bitcoin (BTC) and Bitcoin Cash (BCH) hash-rate oscillations and consider whether we can learn any lessons from history.

Please click here to download a PDF version of this report
Overview
Although there are many crypto tokens, the number of proof-of-work tokens, with their own set of miners, is surprisingly small — so having two significant proof-of-work tokens that share the same hashing algorithm is quite rare. There appear to be three examples of significant hash-rate oscillations caused by this kind of setup:
| Year | Coins | Hashing algorithm |
| 2014 | Litecoin (LTC) vs Dogecoin (DOGE) | Scrypt |
| 2016 | Ethereum (ETC) vs Ethereum Classic (ETC) | EtHash |
| 2017 | Bitcoin (BTC) vs Bitcoin Cash (BCH) | SHA256 |
(Source: BitMEX Research)
A comparison of the 2014 Litecoin (LTC) versus Dogecoin (DOGE) hash-rate oscillations with the 2017 Bitcoin (BTC) versus Bitcoin Cash (BCH) oscillations may reveal some lessons.
In early 2014, Dogecoin enjoyed a sudden, meteoric increase in price (figure 1). Its mining incentives increased quickly and this attracted significant hash-rate. The consequences resembled those of Bitcoin Cash’s infamous emergency difficulty adjustment (EDA), which resulted in sharp drops in mining difficulty and made Bitcoin Cash’s mining incentives higher than Bitcoin’s for short periods. Both instances caused sharp swings in the hash rate and network distribution between the respective coins.
We will look back at the 2014 incident with the help of some charts of hash-rate oscillation to see what it has to tell us about the swings in hash rate between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash, which many are tracking on the fork.lol website.
Mining incentives vs. the difficulty adjustment
The hash-rate distribution between two tokens with the same hashing algorithm should, in theory, be allocated in proportion to the total value of mining incentives on each respective chain. Mining incentives can be thought of as the USD value of both expected block rewards and transaction fees in any given period of time.
Even when token prices, block rewards, and transaction fee levels are temporarily stable, within difficulty adjustment periods further oscillations can occur because miners may switch to more profitable tokens with lower difficulty until the difficulties of the two tokens achieve equilibrium.
Litecoin vs. Dogecoin in 2014
Dogecoin enjoyed a large price rally in early 2014 and then began to challenge Litecoin for the title of the highest hash-rate Scrypt-based token. Litecoin has a two-and-a-half-minute block target time and its difficulty adjusts every three and a half days. Dogecoin has a one-minute target time and at the start of 2014 had a four-hour difficulty adjustment period.
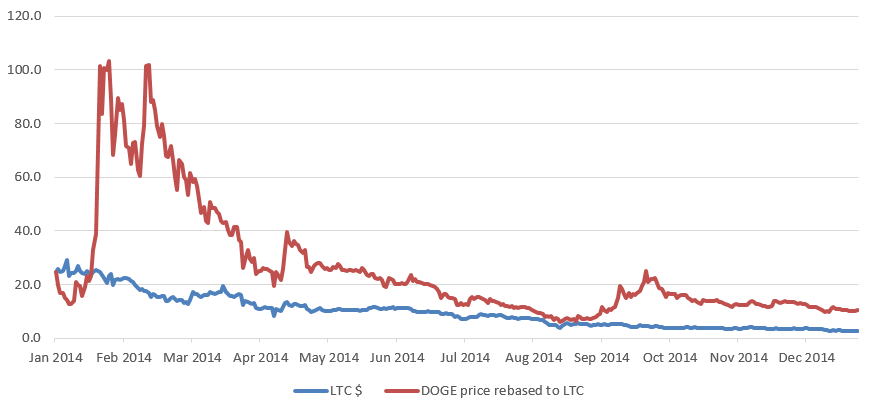
Figure 1: Litecoin (LTC) versus Dogecoin (DOGE) price chart for 2014 (in USD). (Source: Coinmarketcap, BitMEX Research)
The Dogecoin price increased much faster than Litecoin in the early part of 2014 although, as figure 2 shows, Dogecoin never really approached Litecoin’s market capitalisation. Despite its lower market capitalisation, Dogecoin’s higher inflation rate meant that miner rewards were often higher, and a majority of the Scrypt hash rate switched over to Dogecoin during some periods.
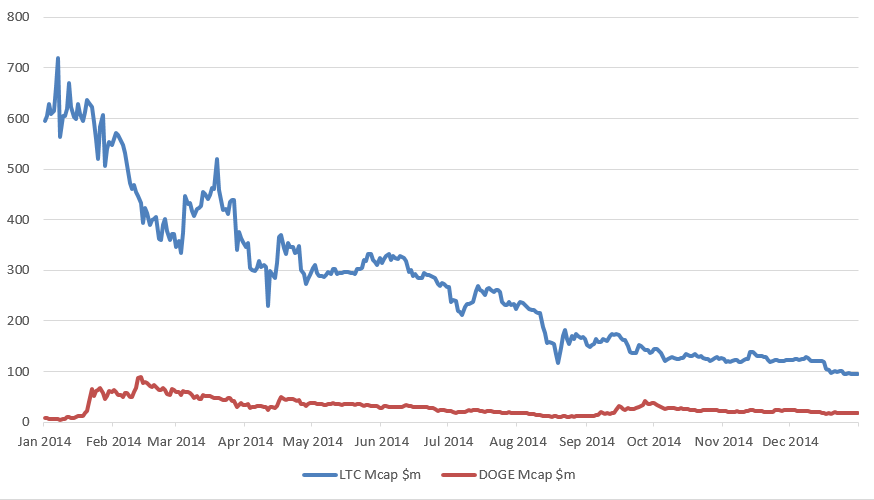
Figure 2: Litecoin (LTC) versus Dogecoin (DOGE) market capitalisation in 2014 (in millions of USD). (Source: Coinmarketcap, BitMEX Research)
Dogecoin’s hash rate exceeded Litecoin’s in late January 2014, as figure 3 indicates. The hash rate swung between the coins for roughly a month as miners switched back and forth.
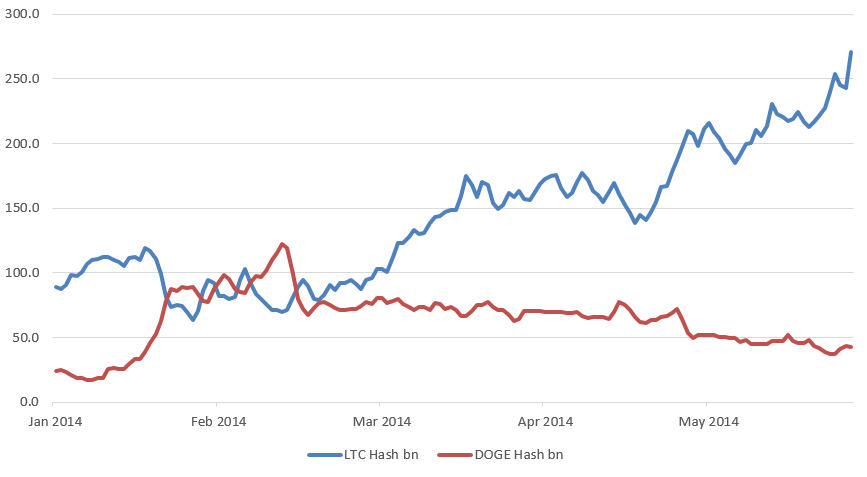
Figure 3: Litecoin (LTC) versus Dogecoin (DOGE) hashrate chart – billion hashes per second – 2014. (Source: Litecoin blockchain, Dogecoin blockchain, BitMEX research)
When, in 2017, Bitcoin Cash had higher mining incentives per unit of time than Bitcoin, many miners switched to Bitcoin Cash, repeating the pattern of 2014. As figure 4 shows, miners followed the money back then too.
A key difference is that even after the difficulty found equilibrium, Dogecoin at times offered higher USD value of mining incentives. In 2017, in contrast, Bitcoin Cash’s incentive lead was always only driven by anomalies in the difficulty adjustment algorithm. Bitcoin always had higher incentives per block than Bitcoin Cash. The higher incentives of Bitcoin Cash came per unit time from its faster blocks and as soon as the difficulty returned to equilibrium, Bitcoin regained its position as the highest incentive SHA256 coin.
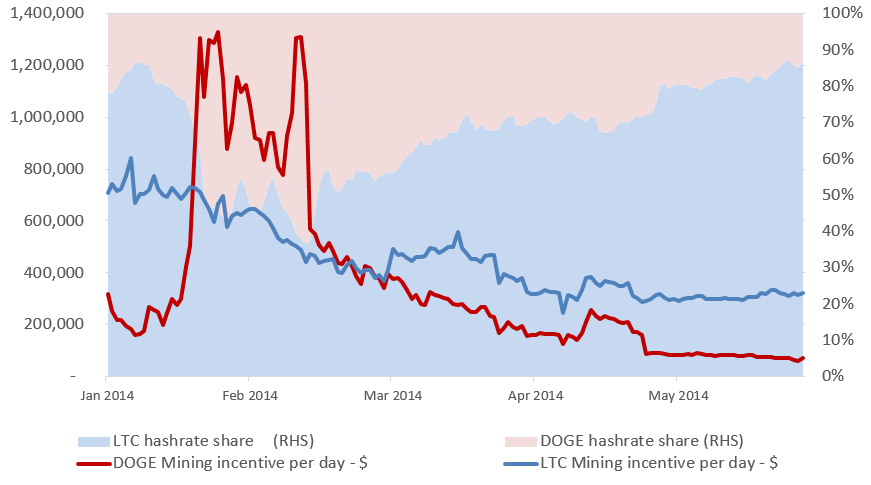
Figure 4: Litecoin (LTC) versus Dogecoin (DOGE) mining incentive (USD per day) versus hash-rate share in 2014. Transaction fees were not included in the mining-incentive calculation. (Source: Coinmarketcap, Litecoin blockchain, Dogecoin blockchain, Dogecoin Github, BitMEX Research)
In order to calculate mining incentives for Dogecoin, we had to consider what occurred in 2014, including six changes to the block reward and two hardforks. These changes are outlined in the table of figure 5.
| Date | Block number | Event type | Expected block reward | Comment | |
| New | Old | ||||
| 14 Feb | 100,000 | Mining-reward change | 250,000 | 500,000 | Random reward between 0 and 500,000 DOGE. |
| 17 Mar | 145,000 | Hardfork | 250,000 | 250,000 | Difficulty retargeting period reduced to one minute from four hours. Randomness removed from block reward. |
| 28 April | 200,000 | Mining-reward change | 125,000 | 250,000 | |
| 15 July | 300,000 | Mining-reward change | 62,500 | 125,000 | |
| 11 Sept | 371,337 | Hardfork | Merged mining with Litecoin enabled. | ||
| 2 Oct | 400,000 | Mining-reward change | 31,250 | 62,500 | |
| 14 Dec | 500,000 | Mining-reward change | 15,625 | 31,250 | |
Figure 5: Dogecoin (DOGE) 2014 event timeline. (Source: Dogecoin blockchain, Dogecoin Github, BitMEX Research)
As figure 5 indicates, on 17 March 2014, Dogecoin changed the difficulty adjustment algorithm, reducing the target time to just one minute (one block) in order to try and alleviate some of the disruption caused by the hash-rate volatility.
Merged mining
In September 2014, Dogecoin activated its merged-mining hardfork. Merged mining is the process by which work done on one chain can also be considered valid work on another chain. Dogecoin can therefore be thought of as an auxiliary blockchain of Litecoin, in that Dogecoin blocks contain an additional data element pointing to the hash of the Litecoin block header, which is considered as valid proof of work for Dogecoin.
The merged-mining system is considered the ultimate solution to the hash-rate oscillation problem, ensuring stability even in the event of sharp token-price movements.
Implications for Bitcoin Cash
The Bitcoin Cash community is unlikely to want to implement merged mining, perhaps for political reasons, in the medium term. Some in the Bitcoin Cash community see Bitcoin as an adversary chain, rather than one with which it should coexist peacefully. Allowing merged mining can be considered the ultimate peace arrangement between two chains. Initially, some in the Dogecoin community were also unhappy about merged mining, but the community eventually realized that it was the best solution to their hash-rate oscillation problem.
However, Bitcoin Cash has recently fixed the EDA issue, which we highlighted in early September as a potential problem. Perhaps the new one-day rolling difficulty adjustment, combined with better price stability, will solve the hash-rate oscillation problem, such that no more fixes are required. If this doesn’t solve the problem, perhaps alternative difficulty adjustment schemes could be tried before merged mining may slowly makes its way onto the agenda.
